×
×
Modern electronics manufacturing faces mounting pressure to balance growing product complexity with compressed development cycles. Modular PCB marking systems address these challenges by enabling rapid equipment reconfiguration—a critical capability when 73% of manufacturers report production delays due to mechanical changeover bottlenecks (IndustryWeek 2023).
Modular marking stations with swappable toolheads and standardized interfaces reduce SMT line setup times by 60—90% compared to fixed systems. This adaptability is vital for automated facilities handling high-mix production, where a Tier 1 EMS provider achieved 47% faster job transitions by implementing vision-guided modular marking workcells. Key automation synergies include:
These capabilities minimize manual intervention and ensure consistent, traceable marking processes across diverse product runs.
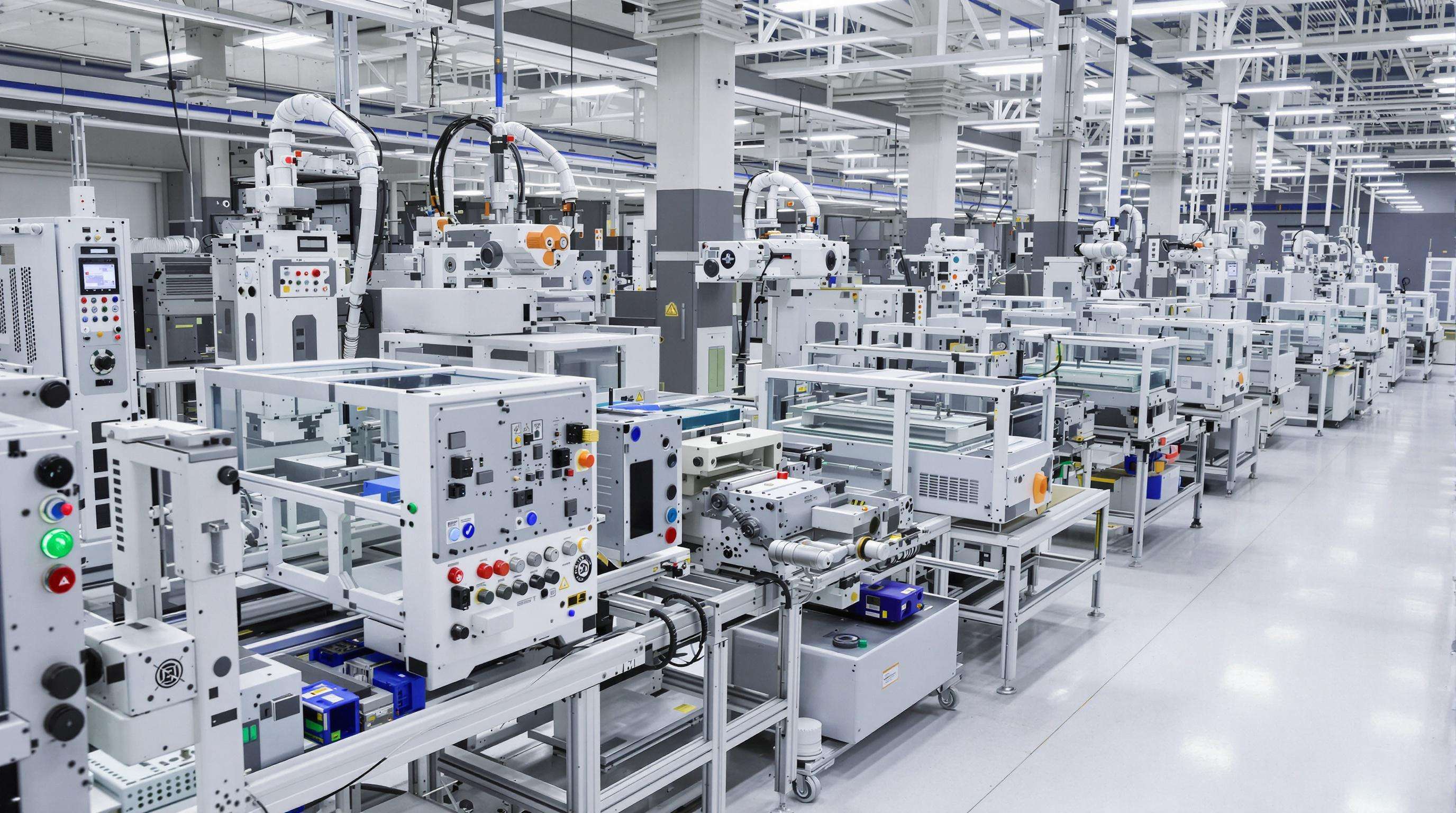

Leading manufacturers align modular marking systems with SMT process engineering protocols to eliminate handoff delays. A 2023 IPC benchmarking study found plants using integrated modular solutions achieved significant performance gains:
| Metric | Improvement vs. Traditional Systems |
|---|---|
| Engineering change adoption | 83% faster |
| Traceability compliance | 92% reduction in errors |
| Machine utilization rate | 41% higher |
This tight integration allows real-time adjustments across stencil printing, component placement, and marking operations—critical for maintaining throughput when managing 15+ product variants per shift.
Modular Design for Manufacture (DFM) prioritizes production efficiency through three foundational principles:
Together, these principles enable 18—22% faster changeover times in SMT environments compared to traditional fixed-configuration systems.
Modular electronics manufacturing systems deliver flexibility through:
This framework reduces capital expenditure for line expansions by 40—60% compared to legacy systems, while maintaining error rates below 0.5% in high-mix PCB assembly.
Modern electronics manufacturing demands systems that adapt faster than traditional dedicated lines. Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems (RMS) now enable modular PCB marking workstations to achieve 68% faster product changeovers compared to fixed automation (ScienceDirect 2021). This agility addresses two key market pressures:
| Production Factor | Traditional Approach | Modular Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Line Reconfiguration Time | 48—72 hours | <8 hours |
| Annual SKU Capacity | 15—20 variants | 100+ variants |
| ROI Period | 3—5 years | 14—18 months |
Leading EMS providers report 32% higher equipment utilization when using RMS-compliant modular marking systems. This shift aligns with industry trends toward smaller batch sizes—87% of PCBA services now handle orders under 500 units (2024 IPC Report).
A recent implementation of modular PCB marking technology delivered measurable gains:
These improvements were achieved through standardized mechanical interfaces and software-defined process parameters, enabling modular PCB marking cells to autonomously adjust for different board dimensions, marking requirements, and traceability protocols. The same study found RMS implementations deliver $740k annual savings per production line (Ponemon 2023).
The debate centers on whether modular systems should prioritize:
Standardization Advocates:
Customization Proponents:
A 2024 MIT Manufacturing Review found hybrid approaches yield optimal results—61% of high-performance manufacturers use standardized modular architectures with configurable software layers. This balances the 83% faster deployment of standardized modules with the 29% efficiency gains from customized process tuning.
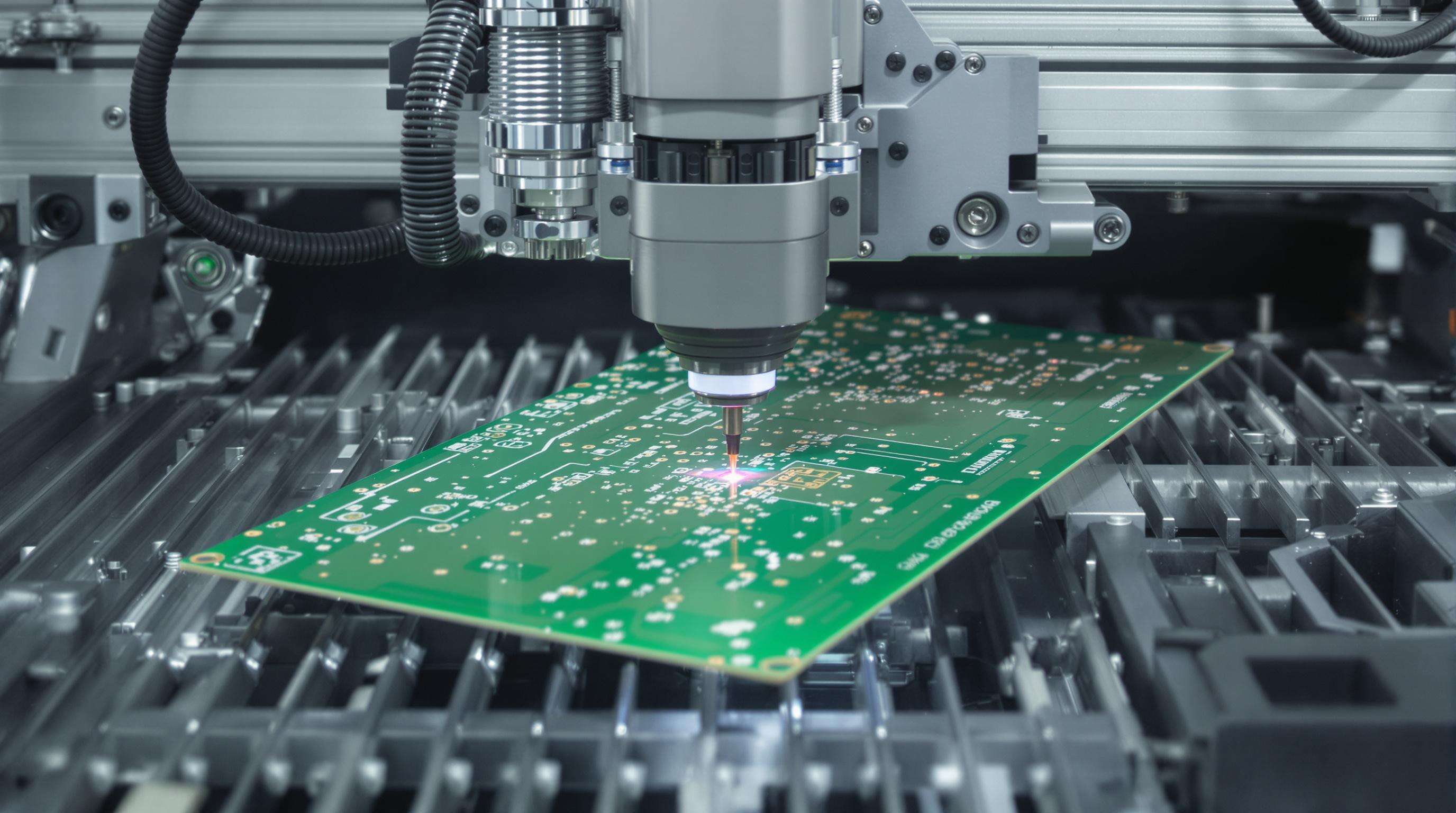
Modern modular PCB marking systems can hit around ±5 microns accuracy thanks to fiber lasers that tweak their power settings and frequencies depending on what material they're working with. A recent IEEE paper from 2023 showed something pretty impressive too these vision systems cut down marking mistakes by nearly two thirds when they spot issues in real time and fix them automatically. What makes these smart workstations stand out is how they check important quality factors such as depth of cut (DOC) measurements and character edge definition (CED) standards right there at the station. Boards only move forward once everything checks out, which means manufacturers save time because they don't have to do those tedious inspections after marking anymore about 92% fewer of them actually.
| Technology | Traditional Marking | Smart Modular Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment Accuracy | ±25 µm | ±5 µm |
| Error Detection Rate | 72% manual | 98% automated |
| Reconfiguration Time | 45—90 minutes | <7 minutes |
Modular workstations equipped with edge computing hardware handle around 14,000 different data points each minute. These include things like laser focal lengths and variations in conveyor speeds. The system can actually predict when components might fail, giving warnings as early as 27 hours ahead of time. We saw this work during a real world test at a PCB factory that makes many different products. Cloud dashboards link various marking settings directly to how well solder joints hold together later on. When sensors pick up any substrate warping, they trigger automatic changes to laser intensity within just 0.02 seconds. This kind of responsiveness makes a big difference in production quality control.
The flexible modular workstation setup is really making waves among electronics manufacturers who need to cut down on product development time. When companies combine modular PCB marking systems with production setups that can be rearranged as needed, they typically manage design changes about 60 percent quicker compared to those stuck with old school fixed automation methods according to Assembly Tech Review last year. This kind of flexibility matters most when moving products from the prototype stage all the way through to actual production runs. Traditional marking equipment just gets in the way at these crucial moments, creating delays that nobody wants.
Modular PCB marking solutions eliminate the need for complete line re-engineering when introducing new board designs. Manufacturers using modular workstations reduced prototype-to-production timelines by 34% through three key capabilities:
Advanced simulation tools now allow virtual testing of modular configurations, reducing physical prototype iterations by up to 50% according to a 2025 industrial machine design study. This digital twin approach enables engineers to optimize workstation layouts before deployment, cutting engineering rework by 18% during new product introductions.
The electronics industry is witnessing a convergence between bespoke manufacturing and scaled production. Modular PCB marking workstations now support economically viable runs as small as 50 units while remaining ready for 10,000-unit orders through:
This dual capability resolves the traditional tradeoff between flexibility and throughput. Leading manufacturers report 27% higher equipment utilization rates when combining low-volume prototyping with high-mix production in modularized facilities, effectively compressing time-to-market across their entire product portfolio.
Modular PCB marking is crucial for enabling rapid reconfiguration of equipment, thereby supporting agile manufacturing processes. This reduces setup times and production delays, critical in high-mix production settings.
Modular systems enhance automation by allowing quick swapping of toolheads, use of machine-readable codes for parameters, and maintaining high positioning accuracy, reducing the need for manual intervention.
The core principles include standardized interfaces for compatibility, minimizing component variations to reduce costs, and layouts focusing on easy serviceability, all of which support agile workflows and fast changeovers.